Understanding Inguinal Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Inguinal hernia, a common medical condition, occurs when soft tissue—often part of the intestine—protrudes through a weak spot or tear in the abdominal wall, specifically in the inguinal canal. This condition primarily affects men, but it can also occur in women. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for proper management and prevention of complications.
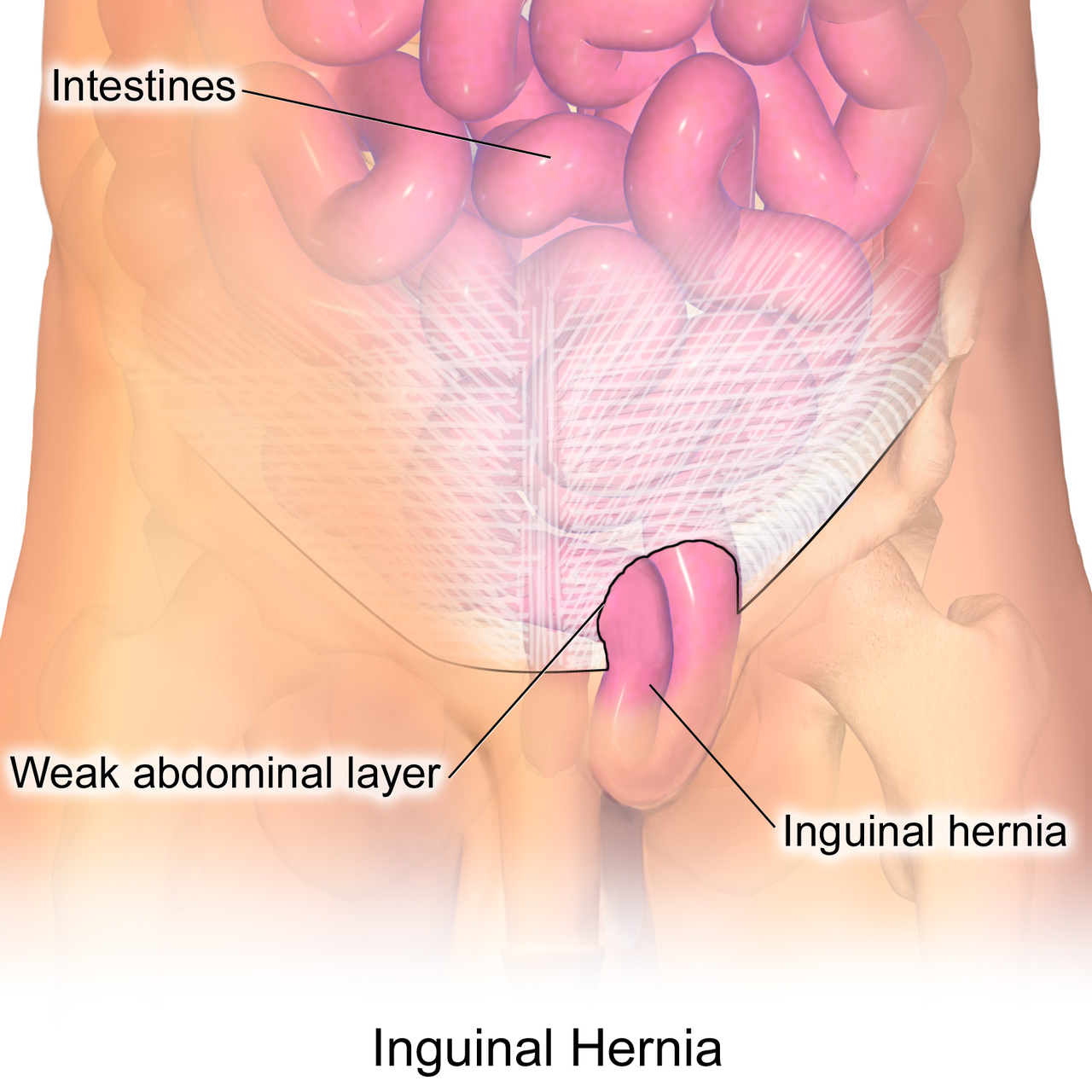
Causes:
The development of an inguinal hernia often stems from a combination of factors. These may include:
1. Weakness in the Abdominal Wall:
Weaknesses in the abdominal wall can be present from birth or develop over time due to aging, heavy lifting, chronic coughing, or straining during bowel movements.
2.Increased Intra-abdominal Pressure:
Activities or conditions that increase pressure within the abdomen, such as obesity, pregnancy, or chronic constipation, can contribute to the development of inguinal hernias.
3. Congenital Factors:
In some cases, inguinal hernias may be congenital, meaning they are present at birth. This can occur due to incomplete closure of the inguinal canal during fetal development.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of an inguinal hernia can vary in severity and may include:
1. Visible Bulge:
The most common symptom is a noticeable bulge in the groin area, which may become more prominent when standing, coughing, or straining.
2. Pain or Discomfort:
Some individuals may experience discomfort or aching in the groin, especially when lifting heavy objects or engaging in physical activity.
3. Pressure or Heaviness:
A sensation of pressure or heaviness in the groin area may accompany the bulge.
4. Swelling or Redness:
Inguinal hernias can cause swelling or redness in the groin or scrotum, particularly if the protruding tissue becomes trapped or incarcerated.
Treatment Options:
The management of inguinal hernias typically involves surgical intervention, although watchful waiting may be appropriate for small, asymptomatic hernias. Surgical options include:
1. Hernia Repair Surgery:
The most common surgical approach for inguinal hernias is hernia repair surgery, which can be performed using open or laparoscopic techniques.
-
Open Hernia Repair
In this approach, the surgeon makes an incision in the groin to access the hernia and repair the weakened abdominal wall.
-
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair:
This minimally invasive technique involves making several small incisions and using a camera and specialized instruments to repair the hernia from within the abdomen.
2. Hernia Mesh:
During surgery, the surgeon may reinforce the weakened area with a synthetic mesh to provide additional support and reduce the risk of recurrence.
3. Non-Surgical Management:
In some cases, particularly for individuals with significant medical comorbidities or who are not suitable candidates for surgery, non-surgical management options such as supportive garments or lifestyle modifications may be recommended to alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Complications:
While inguinal hernias are not typically life-threatening, complications can arise if the protruding tissue becomes trapped or incarcerated, leading to:
-
Strangulation:
In severe cases, the blood supply to the trapped tissue may be compromised, resulting in tissue death (strangulation), which requires emergency medical attention.
-
Obstruction
A hernia can also lead to bowel obstruction if a portion of the intestine becomes trapped within the hernia sac, preventing the passage of stool.
Conclusion
Inguinal hernias are a common medical condition characterized by the protrusion of soft tissue through a weakened area of the abdominal wall. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for inguinal hernias is essential for timely diagnosis and appropriate management. While surgical repair is the primary treatment approach, careful monitoring and lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of complications and improve overall quality of life for individuals with inguinal hernias.
