A fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between two organs or vessels that do not normally connect. This condition can occur in various parts of the body, and it often results from injury, infection, inflammation, or surgery. Fistulas can form between organs such as the intestines, bladder, vagina, and rectum, or between blood vessels.
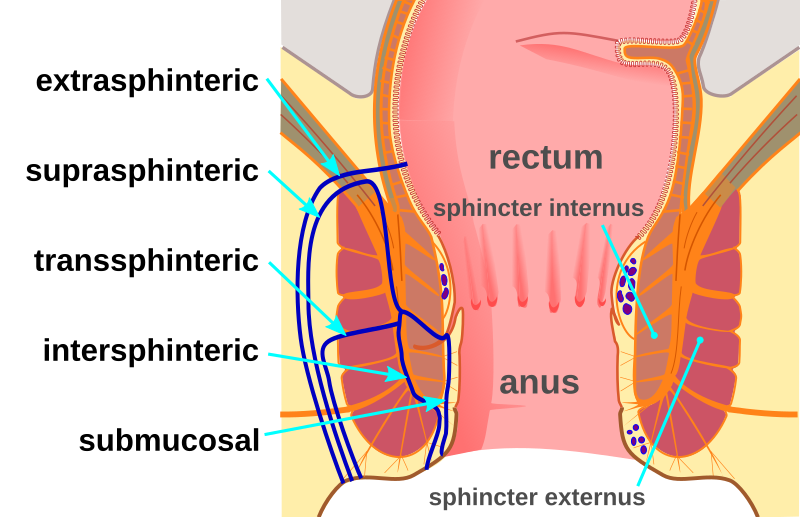
Here are a few examples of different types of fistulas:
- 1.Gastrointestinal Fistula: This type of fistula can occur between different parts of the digestive tract, such as between the intestine and the skin. It may lead to the abnormal passage of digestive fluids and contents to the outside of the body.
- 2.Vesicovaginal Fistula (VVF): This is a fistula between the bladder and the vagina. It can result in the involuntary passage of urine into the vagina and is often associated with obstetric complications during childbirth.
- 3.Rectovaginal Fistula (RVF): This is a fistula between the rectum and the vagina, leading to the passage of stool into the vagina. It can be caused by factors such as childbirth injuries, inflammatory bowel disease, or surgical complications.
- 4.Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF): This type of fistula involves an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein. It can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired due to trauma, surgery, or certain medical conditions.
- 5.Enterocutaneous Fistula: This occurs when there is an abnormal connection between the intestine and the skin, leading to the discharge of intestinal contents through an opening in the abdominal wall.
Treatment for fistulas depends on the underlying cause, location, and severity. Surgical intervention is often necessary to correct the abnormal connection and restore normal bodily functions. In some cases, medical management may be employed to address underlying conditions, such as infection or inflammation, before surgical repair.
It's important for individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of a fistula, such as persistent drainage, pain, or changes in bowel or bladder habits, to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
