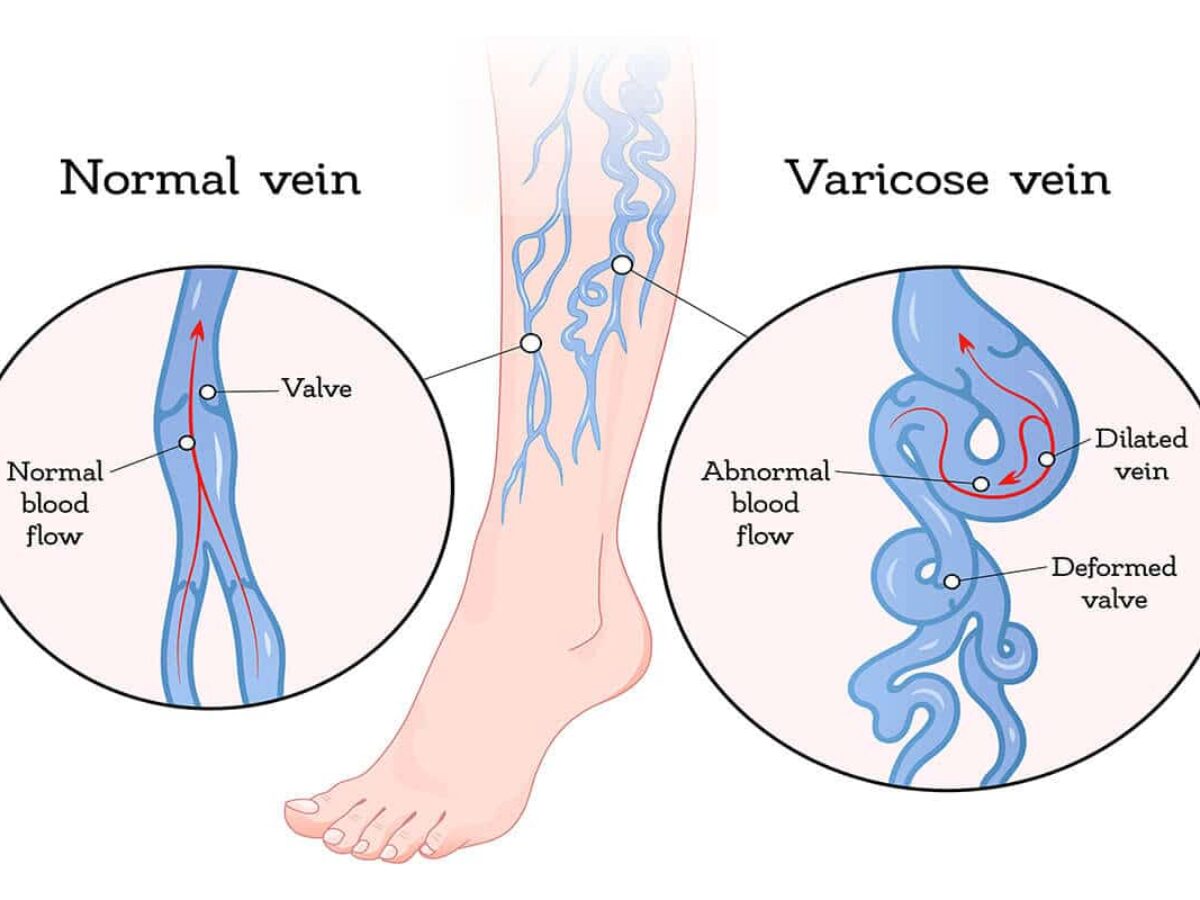
Varicose veins are swollen, twisted veins that often appear blue or dark purple. They usually occur in the legs, but can also form in other parts of the body. Varicose veins are a common condition, and they can be caused by weakened valves in the veins or increased pressure on the veins.
Here are some key points about varicose veins:
1.Causes:
- Weak Valves: Veins have one-way valves that help blood flow back to the heart. If these valves weaken or become damaged, blood can pool in the veins, causing them to enlarge.
- Genetics: A family history of varicose veins can increase the risk of developing them.
- Age: The risk of varicose veins increases with age.
2.Symptoms
- Visible Veins: The most obvious sign is the appearance of swollen, twisted veins that are often visible just beneath the surface of the skin.
- Aching or Pain: Some people with varicose veins may experience aching or pain, especially after standing for long periods.
3.Risk Factors:
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop varicose veins.
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy can increase the pressure on the veins in the pelvis and legs, leading to the development of varicose veins.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the veins.
4.Prevention and Treatment:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve circulation and help prevent varicose veins.
- Elevating Legs: Keeping the legs elevated when resting can reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help support the veins and alleviate symptoms.
- Medical Procedures: In more severe cases, medical procedures such as sclerotherapy, laser therapy, or vein stripping may be recommended.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options if you suspect you have varicose veins or are experiencing related symptoms. They can provide guidance based on your specific situation.
