A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure in which a woman's uterus is removed. The uterus is the organ where fetal development occurs during pregnancy. A hysterectomy may involve the removal of the entire uterus or only a portion of it, and in some cases, it may also involve the removal of other adjacent reproductive organs, such as the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
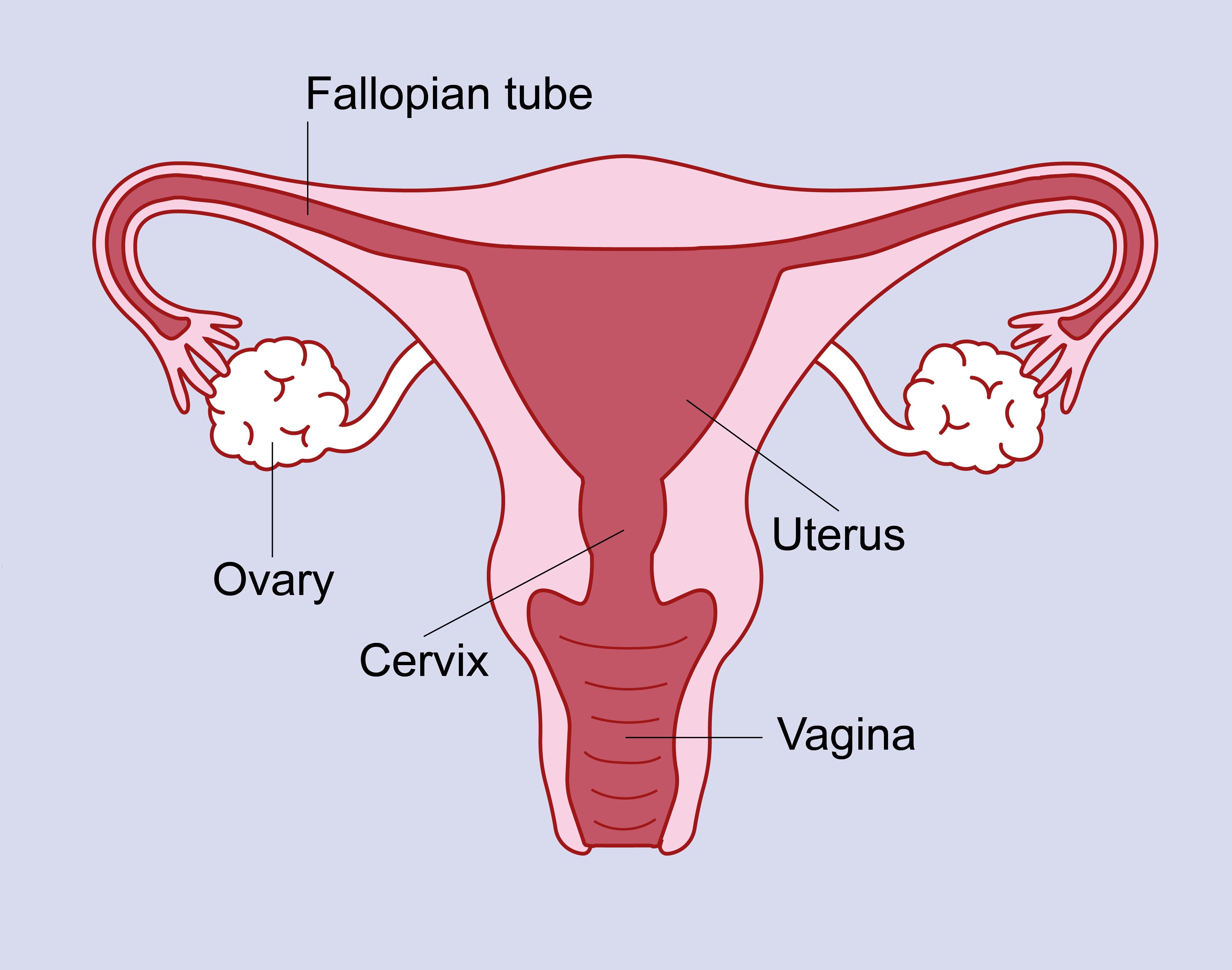
There are different types of hysterectomy procedures:
1.Total Hysterectomy: Involves the removal of the entire uterus, including the cervix.
2.Subtotal or Partial Hysterectomy: Involves the removal of the upper part of the uterus, but the cervix is left intact.
3.Radical Hysterectomy: In addition to removing the uterus, this procedure involves the removal of surrounding tissues, such as the upper part of the vagina and supporting tissues. It is often performed in cases of certain cancers.
Hysterectomies can be performed through various methods, including:
1.Abdominal Hysterectomy: The uterus is removed through an incision made in the abdominal wall.
2.Vaginal Hysterectomy: The uterus is removed through the vaginal canal without making an external incision.
3. Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Also known as minimally invasive surgery, this method involves using small incisions and a camera to guide the surgeon.
Hysterectomies are typically performed for various medical reasons, including:
- Uterine fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
- Uterine cancer: Cancer of the uterus.
- Chronic pelvic pain: Severe and persistent pain in the pelvic region.
- Uterine prolapse: When the uterus descends into the vagina.
- Abnormal bleeding: Uncontrolled or irregular menstrual bleeding.
It's important to note that a hysterectomy is a major surgical procedure and has both physical and emotional implications. Recovery time varies depending on the type of hysterectomy performed and individual factors. Before deciding on a hysterectomy, women should thoroughly discuss their medical condition, treatment options, and potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider. Additionally, it's crucial to consider the impact of the procedure on fertility and hormonal balance, especially if the ovaries are also removed.
