Introduction
Laparoscopic myomectomy is a surgical procedure designed to remove uterine fibroids through small incisions in the abdomen. Fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are noncancerous growths that develop within the muscle tissue of the uterus. While many women with fibroids may not experience symptoms, others may suffer from pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, urinary frequency, or reproductive issues such as infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
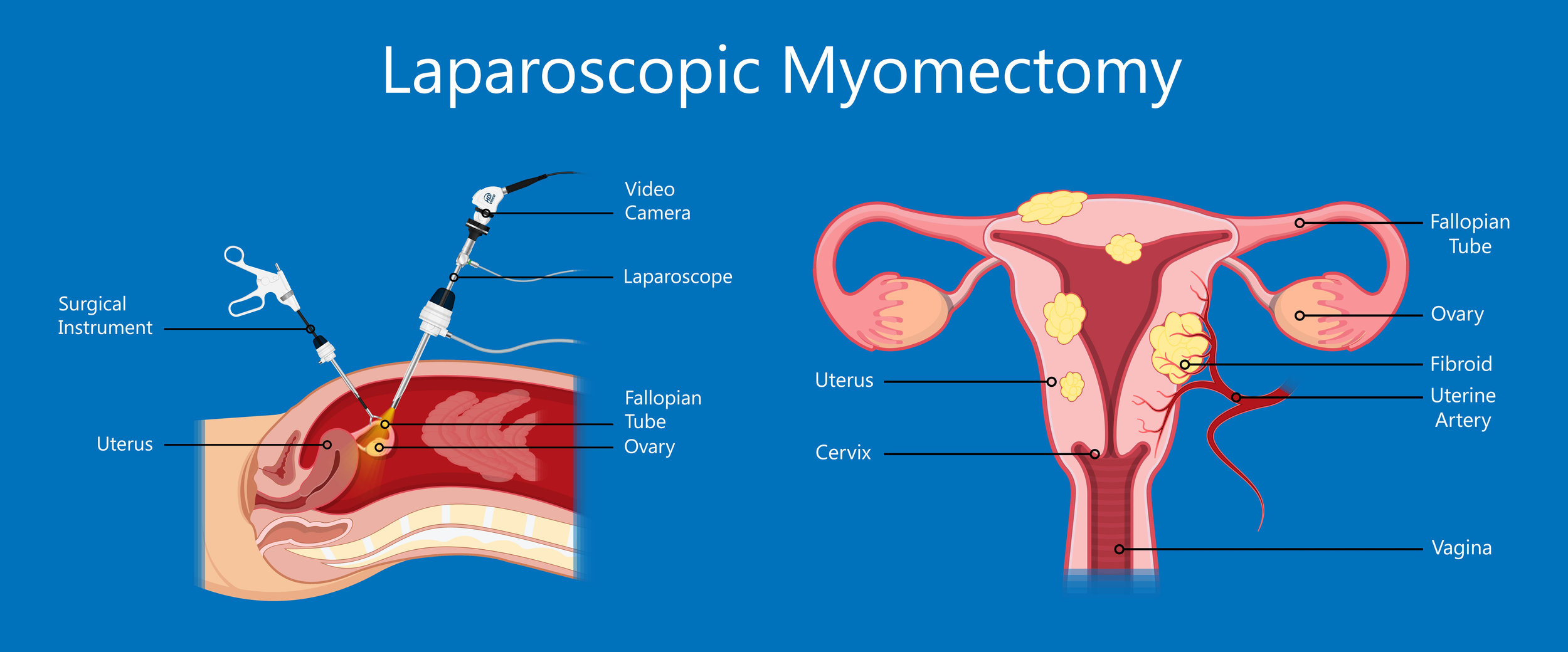
Purpose of Laparoscopic Myomectomy:
The primary goal of laparoscopic myomectomy is to alleviate symptoms associated with fibroids while preserving the uterus and maintaining reproductive function. Unlike hysterectomy, which involves the removal of the entire uterus, myomectomy targets only the fibroids, allowing women to retain their fertility and reproductive potential.
Procedure Overview:
Laparoscopic myomectomy is performed under general anesthesia. During the procedure, the surgeon makes several small incisions in the abdomen, typically around the navel area. Carbon dioxide gas is then used to inflate the abdominal cavity, providing space for the surgeon to work. A laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera and light source, is inserted through one of the incisions, allowing the surgeon to visualize the internal structures of the pelvis. Specialized instruments are used to locate and remove the fibroids while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. Once the fibroids are excised, the incisions are closed, and the carbon dioxide gas is released.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Myomectomy:
Laparoscopic myomectomy offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
1. Minimally Invasive:
Laparoscopic myomectomy requires only small incisions, resulting in less pain, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery compared to open surgery.
2. Preservation of Fertility:
By selectively removing fibroids while leaving the uterus intact, laparoscopic myomectomy preserves fertility and allows women to pursue pregnancy if desired.
3. Shorter Hospital Stay:
Most patients undergoing laparoscopic myomectomy are able to go home the same day or within 24 hours of the procedure, minimizing the disruption to their daily lives.
4. Reduced Risk of Complications:
The smaller incisions and decreased manipulation of surrounding tissues during laparoscopic myomectomy result in a lower risk of complications such as infection, adhesions, and hernias.
Indications for Laparoscopic Myomectomy:
Laparoscopic myomectomy may be recommended for women who:
- Experience symptomatic fibroids, including pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, or pressure symptoms.
- Desire to preserve fertility and avoid the need for hysterectomy.
- Have fibroids that are causing infertility or recurrent miscarriages.
- Prefer a minimally invasive approach to surgery.
Patient Evaluation and Preoperative Preparation:
Before undergoing laparoscopic myomectomy, patients will undergo a thorough evaluation to assess their overall health and suitability for surgery. This may include:
- Medical history review
- Physical examination
- Pelvic ultrasound or MRI to assess the size, number, and location of fibroids
- Laboratory tests, including blood count and coagulation profile
- Discussion of surgical risks, benefits, and alternatives
In addition, patients may be advised to:
- Discontinue certain medications that increase the risk of bleeding, such as aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Avoid eating or drinking after midnight on the night before surgery
- Arrange for transportation to and from the hospital on the day of surgery
- Follow any additional instructions provided by their healthcare provider
Surgical Technique:
During laparoscopic myomectomy, the surgeon employs advanced techniques to locate and remove fibroids while minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues. Key steps in the surgical procedure may include:
Access and Visualization: The surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen and inserts trocars (hollow tubes) through which the laparoscope and surgical instruments are introduced. Carbon dioxide gas is used to create a pneumoperitoneum, allowing for better visualization of the pelvic organs.
Fibroid Localization: Using the laparoscope and specialized instruments, the surgeon locates and identifies the fibroids within the uterus. Fibroids may be located on the outer surface (subserosal), within the muscle wall (intramural), or protruding into the uterine cavity (submucosal).
Myomectomy: Once the fibroids are identified, the surgeon carefully dissects the tissue surrounding each fibroid to expose its blood supply. The fibroid is then excised from the uterus using techniques such as cutting, shaving, or morcellation (fragmentation into smaller pieces). Hemostasis (control of bleeding) is achieved using electrocautery, sutures, or other techniques as needed.
Closure and Recovery: After all fibroids have been removed, the surgeon ensures hemostasis and inspects the pelvic cavity for any signs of bleeding or injury. The incisions are then closed with sutures or surgical glue, and dressings are applied as needed. The patient is transferred to the recovery area and monitored closely for any signs of complications.
Postoperative Care and Recovery:
Following laparoscopic myomectomy, patients can expect a relatively quick recovery compared to traditional open surgery. Most patients are able to resume normal activities within a few days to weeks, depending on the size and number of fibroids removed. The following postoperative care guidelines may help facilitate recovery:
Pain Management:
Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort during the initial recovery period.
Activity Restrictions:
Patients are typically advised to avoid heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, and sexual activity for a specified period following surgery to allow the incisions to heal properly.
Follow-Up Visits:
Patients will have follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor their recovery, evaluate surgical outcomes, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
Fertility Considerations:
While laparoscopic myomectomy preserves fertility in most cases, patients should discuss their reproductive goals and timeline with their healthcare provider to optimize their chances of conception after surgery.
Symptoms Monitoring:
Patients should be vigilant for any signs of complications such as excessive bleeding, fever, or worsening pelvic pain and seek medical attention promptly if they occur.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopic myomectomy is a safe and effective treatment option for women with symptomatic fibroids who wish to preserve their fertility and avoid hysterectomy. By utilizing minimally invasive techniques, laparoscopic myomectomy offers patients faster recovery, fewer complications, and improved quality of life compared to traditional open surgery. With careful patient selection, thorough preoperative evaluation, and skilled surgical expertise, laparoscopic myomectomy can provide long-lasting relief from fibroid-related symptoms while preserving the uterus and reproductive function.
